MoBioFood Research Group published a new paper in the journal Disease Models and Mechanisms
Identification of a nutrient sensing transcriptional network in monocytes by using inbred rat models of cafeteria diet
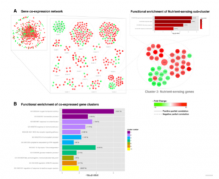
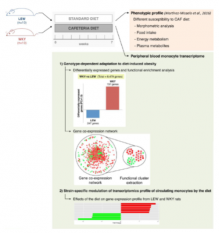
Obesity has reached pandemic levels worldwide. The current models of diet-induced obesity in rodents use predominantly high-fat based diets that do not take into account the consumption of variety of highly palatable, energy dense foods that are prevalent in Western society. We and others have shown that cafeteria diet (CAF) is a robust and reproducible model of human metabolic syndrome with tissue inflammation in the rat. We have previously shown that inbred rat strains such as Wistar Kyoto (WKY) and Lewis (LEW) show different susceptibilities to CAF diets with distinct metabolic and morphometric profiles. Here we show a difference in plasma MCP-1 levels and investigate the effect of CAF diet on peripheral blood monocyte transcriptome as powerful stress-sensing immune cells in WKY and LEW rats. We found that 75.5% of the differentially expressed transcripts under CAF diet were up-regulated in WKY rats and were functionally related to the activation of the immune response. Using a gene co-expression network constructed from the genes differentially expressed between CAF diet-fed LEW and WKY rats, we identified the Acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family member 2 (Acss2) as a hubgene for a nutrient sensing cluster of transcripts in monocytes. Acss2 genomic region is significantly enriched for previously established metabolism quantitative trait loci in the rat. Notably, monocyte expression levels of Acss2 significantly correlated with plasma glucose, triglyceride, leptin and NEFA levels as well as morphometric measurements such as body weight and the total fat following CAF in the rat. These results show the importance of the genetic background in nutritional genomics and identify inbred rat strains as potential models for CAF-induced obesity.